Commonly Misunderstood Items on Electric Motor Nameplates
January 11, 2017
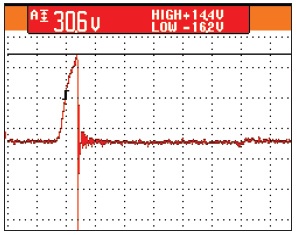
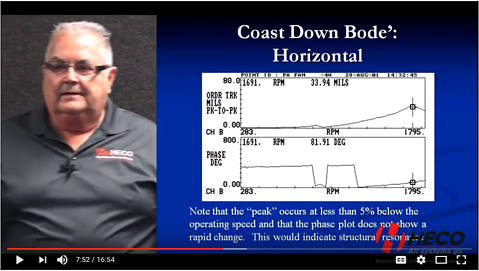
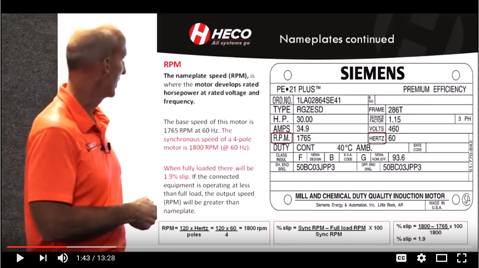
Todd A. Hatfield – Vice President of Engineering & Repair, HECO This is the third article (video) in a series of articles on The Basics of AC Induction Motors. The first video explored the basic principles of AC Induction motors focusing on magnetism, electromagnetic induction, AC current, and rotating magnetic fields. The second segment discussed …