Bearing Failures on VFD Controlled Electric Motors - HECO
January 3, 2017
Shaft currents can have a destructive effect on electric motor bearings. This article, with information from our friends at AEGIS Shaft Grounding Rings, is intended to inform professionals about these voltages and their effects on bearings in electric motors.
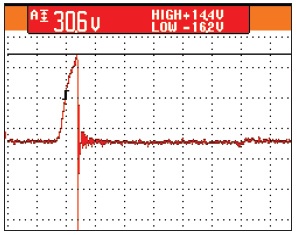
Because of the high-speed switching frequencies in PWM inverters, variable frequency drives induce shaft currents in AC motors. The switching frequencies of insulated-gate bipolar transistors (IGBT) used in these drives produce voltages on the motor shaft during normal operation through parasitic capacitance between the stator and rotor. These voltages, which can register 10-40 volts peak, are easily measured by touching an oscilloscope probe to the shaft while the motor is running. (Reference: NEMA MG1 Section 31.4.4.3)
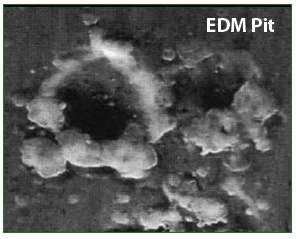
Once these voltages reach a level sufficient to overcome the dielectric properties of the bearing grease, they discharge along the path of least resistance — typically the motor bearings — to the motor housing. During virtually every VFD switching cycle, induced shaft voltage discharges from the motor shaft to the frame via the bearings, leaving a small fusion crater (fret) in the bearing race. When this event happens, temperatures are hot enough to melt bearing steel and severely damage the bearing lubrication.

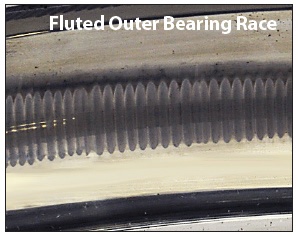
These discharges are so frequent (millions per hour) that before long the entire bearing race becomes marked with countless pits known as frosting. A phenomenon known as fluting may occur as well, producing washboard-like ridges across the frosted bearing race. Fluting causes excessive noise and vibration, and in heating, ventilation, and air-conditioning systems, it is magnified and transmitted by the ducting. Regardless of the type of bearing or race damage that occurs, the resulting motor failure often costs many thousands or even tens of thousands of dollars in downtime and lost production.
Failure rates vary widely depending on many factors, but evidence suggests that a significant portion of failures occur only 3 to 12 months after system startup. Because many of today’s AC motors have sealed bearings to keep out dirt and other contaminants, electrical damage has become the most common cause of bearing failure in AC motors with VFDs.
Here is a video showing you more detail on these issues:
Posted in Equipment Management, Predictive